
What is Automation in Food Processing? | A Comprehensive Guide
Automation in food processing refers to the use of control systems, machinery, robotics, and software to operate equipment and manage tasks in the production of food and beverages with minimal human intervention. This technological evolution moves beyond simple mechanization—where machines assist human labor—to create integrated, intelligent systems that can handle complex sequences from raw material handling to packaging and dispatch. The primary goals are to enhance efficiency, ensure unparalleled consistency and safety, improve scalability, and reduce operational costs. In an industry where precision, hygiene, and speed are paramount, automation has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
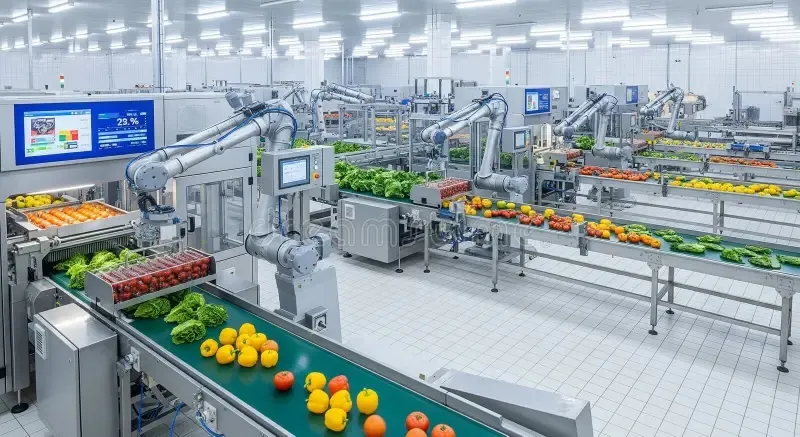

Core Components of Food Processing Automation
The architecture of automation in this sector is built on several interconnected technological pillars.
1. Sensing and Inspection Systems
These are the "eyes" of the operation. Advanced sensors (weight, temperature, vision) and inspection systems (like X-ray and metal detectors) continuously monitor product quality and safety. Machine vision systems, for instance, can inspect thousands of items per minute for defects, color, size, or shape, ensuring only products meeting strict standards proceed.

2. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Robotics
PLCs are the industrial computers that control machinery based on programmed logic, managing everything from conveyor speed to mixer cycles. Collaborative robots (cobots) are increasingly deployed for delicate tasks like packing, palletizing, or even butchery, working safely alongside humans.
3. Integrated Software and Data Analytics
This is the "brain." Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) software collect real-time data from the plant floor. This enables process optimization, predictive maintenance, and full traceability—a critical factor for food safety recalls.
Key Applications in the Food Industry
Automation permeates nearly every stage of food production.
| Processing Stage | Automation Technology Used | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Sorting & Grading | Optical sorters, NIR sensors, AI-powered vision systems | High-speed, consistent quality segregation |
| Processing & Cooking | Automated cookers, fryers, and ovens with precise PLC control | Exact repeatability, optimal product texture and taste |
| Assembly & Packaging | Robotic pick-and-place, automated filling, sealing, and labeling machines | Increased speed, reduced contamination, flexible packaging lines |
| Palletizing & Logistics | Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), robotic palletizers | Reduced physical strain, efficient warehouse management |
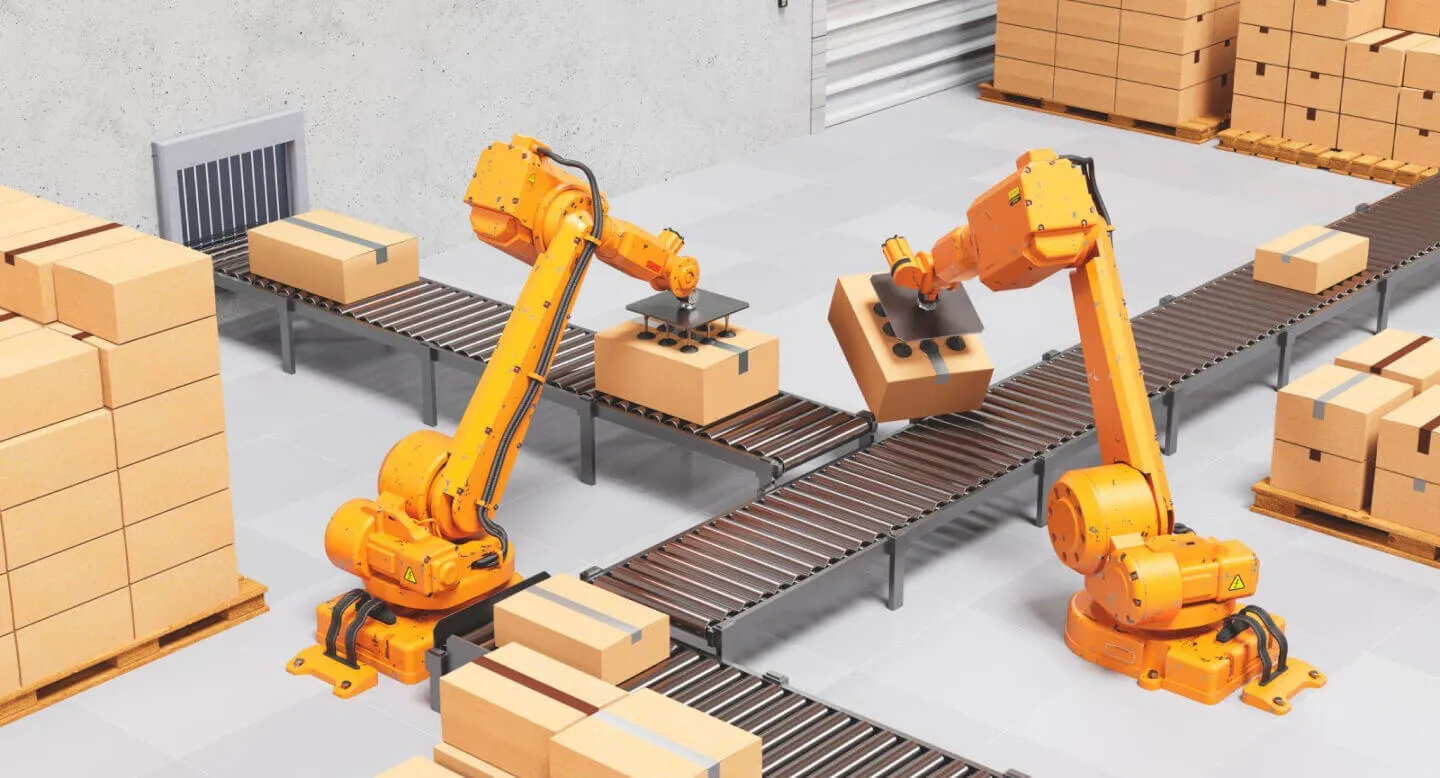

Major Benefits and Impacts
Enhanced Food Safety and Traceability
Automation minimizes human contact with food, reducing contamination risks. Digital record-keeping allows for complete farm-to-fork traceability in seconds.
Unmatched Consistency and Quality
Machines perform tasks identically every time, eliminating human error and variability, resulting in uniform product quality.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Automated lines operate 24/7 with higher throughput and less waste, significantly lowering per-unit costs over time.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite its advantages, automation faces hurdles like high initial capital investment, the need for skilled technicians, and the complexity of handling highly variable natural products. The future points towards Hyper-Automation—the integration of AI and the Internet of Things (IoT) to create self-optimizing "smart factories." AI will enable systems to adapt recipes in real-time based on raw material inputs, while IoT sensors will facilitate predictive maintenance, preventing downtime.
Summary
Automation in food processing is the strategic implementation of technology to control production processes, elevating the industry through superior efficiency, safety, and quality. It encompasses robotics, sensing, and data analytics to manage tasks from sorting to packaging. While challenges exist, the trend towards intelligent, connected systems promises to make food manufacturing more resilient, transparent, and responsive to global demands.
