
Understanding Automated Welding Machine Price Factors
The decision to invest in an automated welding system is a significant one for any manufacturing or fabrication operation. A primary concern for most businesses is the automated welding machine price. This cost is not a single figure but a spectrum, influenced by a complex interplay of factors ranging from technical specifications to brand reputation. Understanding these variables is crucial for making an informed investment that balances upfront expenditure with long-term productivity gains and return on investment (ROI).
Key Factors Influencing Automated Welding Machine Prices
The price of an automated welding machine can vary dramatically, from tens of thousands of dollars for a basic system to several hundred thousand dollars for a fully integrated, robotic cell. The final cost is determined by several core components and capabilities.
1. Type of Automation and System Configuration
The level of automation is the most significant price determinant. Systems range from simple mechanized setups to complex, multi-axis robotic cells.
- Mechanized Welding Systems: These include tractor-mounted torches or fixed torches with moving workpieces (e.g., rotators or positioners). They are excellent for long, straight seams or circular welds and represent the lower end of the price spectrum.
- Robotic Welding Cells: These feature an articulated robotic arm, typically with 6 axes of movement, offering unparalleled flexibility.
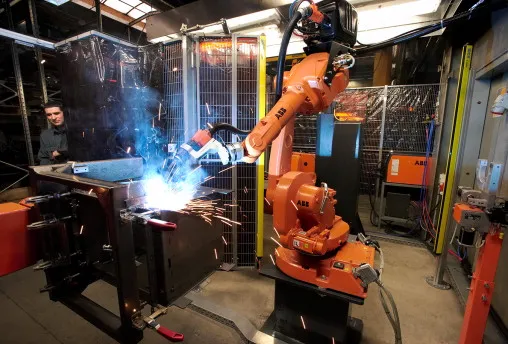 The price includes the robot, controller, welding power source, and often peripherals like a teach pendant.
The price includes the robot, controller, welding power source, and often peripherals like a teach pendant. - Fully Integrated Systems: These are turnkey solutions that may include multiple robots, advanced material handling (e.g., gantry systems), sophisticated sensors (vision systems, seam trackers), and complete safety enclosures. These command the highest prices.
2. Welding Process Technology
The specific welding process the machine is designed for directly impacts its cost. Different processes require different power sources and peripherals.
| Welding Process | Typical Applications | Relative Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG) | General fabrication, automotive | Medium |
| Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG) | Aerospace, precision piping, exotic metals | High (requires more precise control) |
| Arc Welding (SAW) | Heavy construction, shipbuilding | Medium to High |
| Laser Welding | High-speed, precision applications (e.g., medical devices) | Very High |
3. Payload Capacity and Reach
The size and strength of the robot or mechanized unit are critical. A robot designed to handle a small welding torch will be less expensive than a heavy-duty model capable of maneuvering a large water-cooled torch and a heavy wire feeder. Similarly, the required reach (the distance the robot can access) influences the size and cost of the arm.
4. Peripherals and Optional Features
The base machine is often just the starting point. The final price is heavily affected by add-ons that enhance capability, quality, and ease of use.
- Seam Tracking & Vision Systems: These allow the robot to adapt to variations in part fit-up, ensuring consistent weld quality. They add a significant premium but reduce programming time and scrap rates.
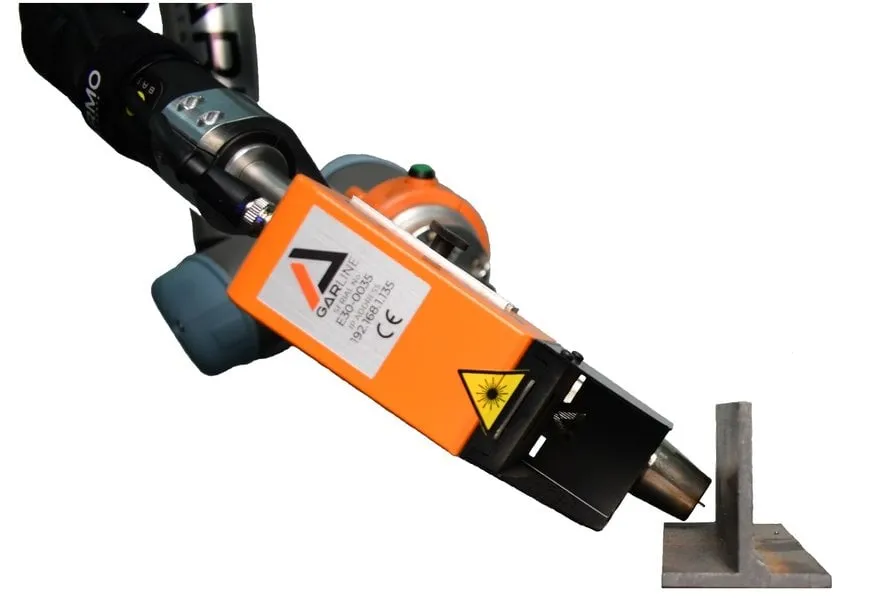

- Tool Changers: Enable a single robot to perform multiple tasks (e.g., welding, grinding, plasma cutting) by automatically switching tools.
- Positioners and Turntables: These move the workpiece into the ideal position for welding, reducing the need for complex robot programming. Their size and weight capacity majorly affect their cost.
- Software Packages: Advanced software for offline programming (OLP) simulation can streamline integration but adds to the initial cost.
5. Brand and Supplier
Established brands like FANUC, Yaskawa (Motoman), KUKA, and ABB often carry a price premium due to their proven reliability, extensive global service networks, and robust software support. Smaller or newer manufacturers may offer more competitive pricing but with potentially varying levels of support and longevity.
Breaking Down the Price Range
While prices are always changing, a general breakdown can be outlined:
| System Type | Estimated Price Range (USD) | What's Typically Included |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Mechanized Setup | $15,000 - $50,000 | Power source, tractor or carriage, basic controller |
| Standard Robotic Welding Cell | $75,000 - $150,000 | Robot, controller, welding package, safety fencing, basic programming |
| High-End Integrated Cell | $150,000 - $300,000+ | Large robot, advanced sensors (seam tracking, vision), material handling (positioners), sophisticated software |
| Custom Laser Welding System | $250,000 - $500,000+ | High-power laser source, specialized robot, safety enclosure, precision controls |
Beyond the Sticker Price: Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The initial purchase price is only part of the financial picture. A truly cost-effective investment considers the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes:
- Installation & Integration: Costs for site preparation, utilities (power, gas), and system programming.
- Training: Investing in operator and programmer training is essential for maximizing uptime and efficiency.
- Maintenance: Routine maintenance (e.g., arm calibration, replacing consumables) and potential repair costs.

- Consumables: Wire, gas, tips, nozzles, and contact tubes.
- Operational Savings: This is the key benefit. Automated welding drastically increases deposition rates, reduces arc-on time, minimizes rework and material waste, and allows for operation with less-skilled labor. These savings must be factored into the ROI calculation.
Conclusion: Making a Strategic Investment
There is no single answer to "How much does an automated welding machine cost?" Instead, the focus should be on defining your application requirements, production volume, and quality goals. By carefully evaluating the factors of system type, process, peripherals, and brand, you can narrow down the options. Most importantly, shift the conversation from mere price to value and ROI. A slightly higher initial investment in a more capable and reliable system with advanced features like seam tracking can lead to far greater long-term profitability through unmatched consistency, speed, and quality. Always consult with multiple reputable integrators to get detailed quotes that include not just equipment but also installation, training, and support.
