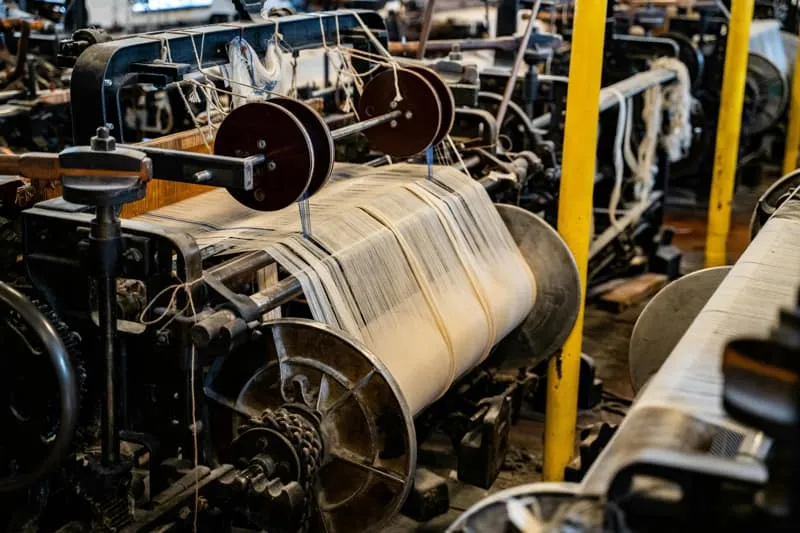
Textile Industry Automation: Revolutionizing Fabric Production
The textile industry, one of the world's oldest manufacturing sectors, has undergone a remarkable transformation through automation. Textile automation refers to the integration of advanced technologies, robotics, computer systems, and artificial intelligence to streamline and optimize various stages of textile production, from raw material processing to finished garment manufacturing.
The Evolution of Textile Automation
Textile automation has evolved significantly since the Industrial Revolution. What began with mechanical looms and spinning frames has now advanced to include sophisticated computer-controlled systems that can operate with minimal human intervention. This evolution has been driven by the need for higher productivity, improved quality control, and reduced labor costs.
Key Historical Milestones
- 18th Century: Mechanical spinning and weaving machines
- 19th Century: Power looms and automated carding machines
- 20th Century: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems
- 21st Century: AI-driven quality control and robotic handling
Core Components of Textile Automation
Automated Spinning Systems
Modern spinning automation includes rotor spinning, air-jet spinning, and compact spinning systems that can operate continuously with minimal human supervision. These systems automatically monitor yarn quality, detect breaks, and maintain consistent tension throughout the production process.
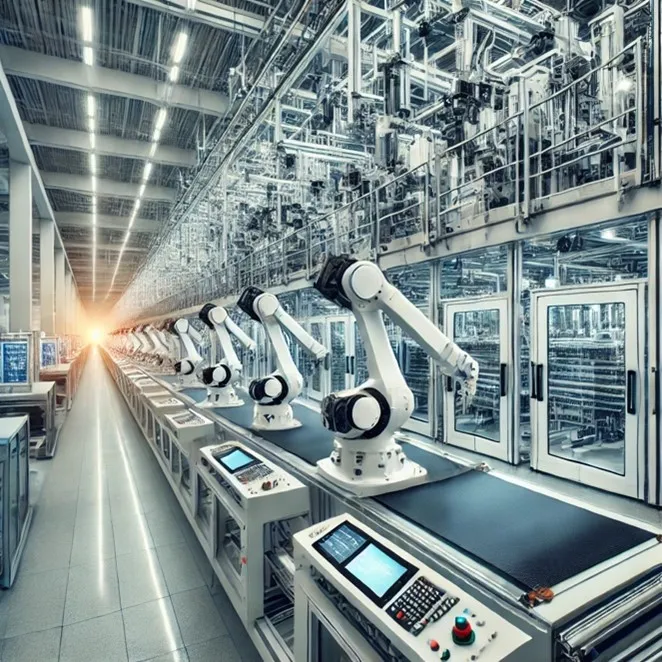

Automated Weaving and Knitting
Computer-controlled looms and knitting machines have revolutionized fabric production. These systems can automatically change patterns, adjust tension, and detect defects in real-time, significantly reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Robotic Material Handling
Robotic systems are increasingly used for material transportation, loading/unloading operations, and packaging. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and robotic arms handle heavy fabric rolls and finished products with precision and speed.
Benefits of Automation in Textile Manufacturing
| Benefit Category | Specific Advantages | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|
| Productivity | 24/7 operation, higher output, reduced downtime | High |
| Quality Control | Consistent quality, real-time defect detection | High |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced labor costs, lower energy consumption | Medium-High |
| Safety | Reduced workplace accidents, ergonomic improvements | Medium |
| Sustainability | Reduced waste, optimized resource usage | Medium |
Advanced Technologies Driving Textile Automation
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI algorithms analyze production data to optimize processes, predict maintenance needs, and improve quality control. Machine learning systems can identify subtle patterns in fabric defects that human inspectors might miss.
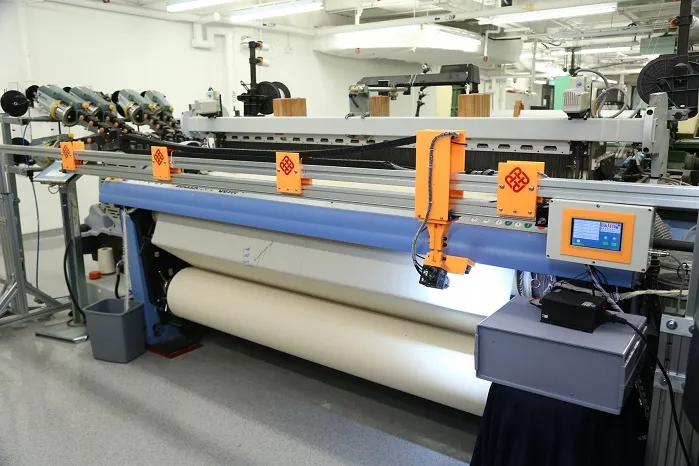

Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT sensors monitor machine performance, environmental conditions, and material flow throughout the production chain. This real-time data enables predictive maintenance and process optimization.
Computer Vision Systems
Advanced camera systems automatically inspect fabrics for defects, color consistency, and pattern accuracy, replacing manual quality control in many applications.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
| Challenge | Potential Impact | Recommended Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| High Initial Investment | Significant capital requirement | Phased implementation, ROI analysis |
| Workforce Training | Skill gap in operating advanced systems | Comprehensive training programs |
| System Integration | Compatibility issues with existing equipment | Modular automation solutions |
| Maintenance Complexity | Higher technical expertise required | Predictive maintenance systems |
Future Trends in Textile Automation
Smart Factories and Industry 4.0
The integration of cyber-physical systems and digital twins will create fully connected textile factories where machines communicate with each other and make autonomous decisions.
Sustainable Automation
Future automation systems will focus on energy efficiency, water conservation, and circular economy principles, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Customization and Mass Personalization
Advanced automation will enable cost-effective production of customized textiles and garments, meeting the growing demand for personalized products.
Global Impact and Market Trends
The global textile automation market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing labor costs in traditional manufacturing hubs and the need for higher production efficiency. Countries like China, India, and Bangladesh are increasingly adopting automated technologies to maintain their competitive edge in the global textile market.
Conclusion
Automation in the textile industry represents a fundamental shift in how fabrics and garments are produced. By combining advanced technologies with traditional textile manufacturing processes, companies can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, quality, and sustainability. As technology continues to evolve, textile automation will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping the future of global textile manufacturing.

