
Plastic Injection Molding Machines: Complete Guide
Introduction to Injection Molding Technology
Plastic injection molding machines represent one of the most critical manufacturing technologies in the modern industrial landscape. These sophisticated machines transform raw plastic materials into precise, complex components used across countless industries, from automotive and medical to consumer goods and electronics. The global injection molding machine market continues to grow, driven by increasing demand for plastic components and technological advancements in manufacturing processes.
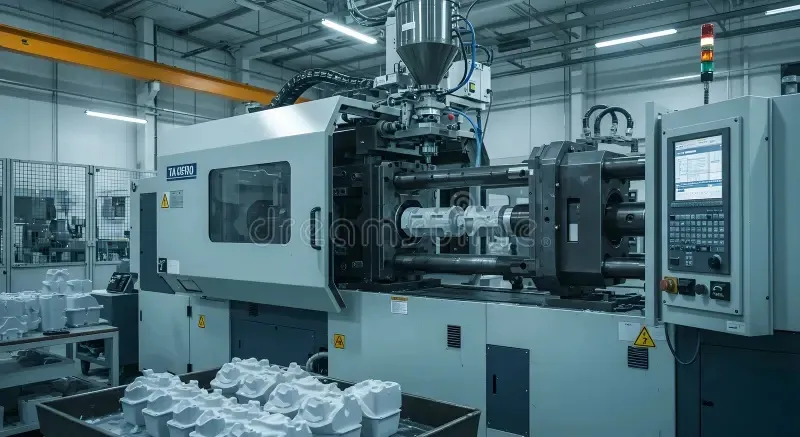

How Injection Molding Machines Work
The Injection Molding Process Cycle
The operation of a plastic injection molding machine follows a precise, repetitive cycle that ensures consistent part quality. The process begins with the feeding of plastic resin pellets into the machine's hopper. These pellets are then transported to the barrel, where they are heated to their melting point. The molten plastic is injected under high pressure into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. Finally, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected, completing the cycle.
Key Components and Their Functions
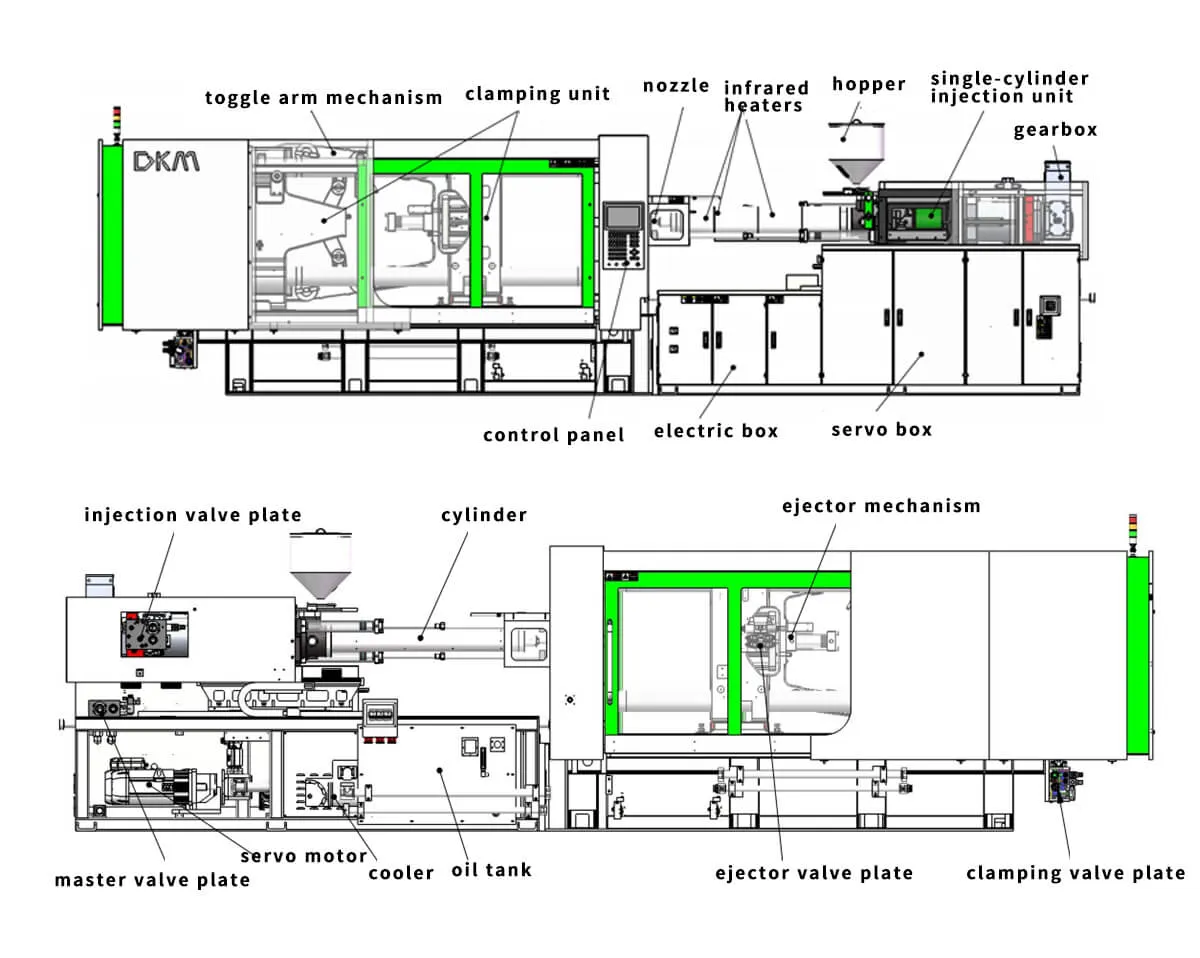
Understanding the major components of an injection molding machine is essential for comprehending its operation. The injection unit consists of the hopper, barrel, screw, and nozzle, responsible for melting and injecting the plastic material. The clamping unit includes the mold, platens, and toggle mechanism, which holds the mold closed during injection. The control system manages all machine parameters, including temperature, pressure, and cycle timing, ensuring optimal performance and part quality.

Types of Injection Molding Machines
Hydraulic Injection Molding Machines
Hydraulic machines represent the traditional workhorses of the injection molding industry. These machines utilize hydraulic systems to generate the clamping force and injection pressure required for the molding process. Known for their robustness and ability to handle large tonnage requirements, hydraulic machines offer excellent power and reliability. However, they typically consume more energy and operate at slower cycle times compared to newer technologies.
Electric Injection Molding Machines
Electric injection molding machines have gained significant popularity due to their energy efficiency and precision. These machines use servo motors to drive all movements, eliminating the need for hydraulic systems. Electric machines offer faster cycle times, higher repeatability, and reduced energy consumption, making them ideal for high-precision applications in industries such as medical devices and electronics.
Hybrid Injection Molding Machines
Hybrid machines combine the best features of both hydraulic and electric technologies. They typically use electric drives for the injection unit while maintaining hydraulic systems for clamping. This configuration provides a balance between energy efficiency, speed, and cost-effectiveness, making hybrid machines a popular choice for many manufacturing applications.
Technical Specifications and Selection Criteria
Key Performance Parameters
Selecting the right injection molding machine requires careful consideration of several critical parameters. Clamping force, measured in tons, determines the machine's ability to keep the mold closed during injection. Shot size indicates the maximum amount of plastic the machine can inject in one cycle. Other important factors include platen size, tie bar spacing, and injection pressure, all of which must align with the specific requirements of the intended application.
| Machine Type | Energy Efficiency | Precision | Initial Cost | Maintenance Requirements | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic | Low | Good | Low | High | Large parts, high volume |
| Electric | High | Excellent | High | Low | Medical, electronics |
| Hybrid | Medium | Very Good | Medium | Medium | General purpose |
Advanced Features and Modern Innovations
Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
Modern injection molding machines are increasingly incorporating Industry 4.0 technologies to enhance productivity and quality control. These smart machines feature IoT connectivity, real-time monitoring systems, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Advanced sensors collect data on machine performance, material conditions, and part quality, enabling manufacturers to optimize processes and reduce downtime through data-driven decision making.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Recent advancements in injection molding technology have focused significantly on improving energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. Modern machines incorporate energy recovery systems, optimized heating elements, and advanced control algorithms that minimize power consumption. Additionally, many manufacturers are developing solutions for processing recycled materials and bioplastics, supporting the circular economy and reducing environmental impact.
Applications Across Industries
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector represents one of the largest consumers of injection molded components. From interior trim pieces and dashboard components to under-the-hood parts and lighting systems, injection molding machines produce countless critical automotive components. The industry demands high precision, durability, and the ability to process engineering-grade materials that can withstand harsh operating conditions.
Medical and Healthcare
In the medical field, injection molding machines manufacture everything from simple syringe components to complex surgical instruments and implantable devices. Medical applications require exceptional precision, cleanroom compatibility, and the ability to process specialized medical-grade materials that meet stringent regulatory requirements. Validation and documentation capabilities are particularly important in this highly regulated industry.
Consumer Products and Packaging
The consumer goods industry relies heavily on injection molding for producing items ranging from household containers and toys to electronic device housings and packaging materials. High-volume production capabilities, fast cycle times, and cost-effectiveness make injection molding ideal for these applications. The ability to create aesthetically pleasing surfaces and incorporate multiple colors further enhances its suitability for consumer products.

Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of injection molding machines. Regular preventive maintenance includes cleaning, lubrication, inspection of critical components, and calibration of control systems. Establishing a comprehensive maintenance schedule helps prevent unexpected downtime, reduces repair costs, and maintains consistent part quality throughout the machine's operational life.
Safety Considerations
Operating injection molding machines requires strict adherence to safety protocols to protect personnel and equipment. Safety measures include proper machine guarding, emergency stop systems, lockout/tagout procedures, and comprehensive operator training. Modern machines incorporate advanced safety features such as light curtains, area scanners, and interlocked guards to minimize risks associated with high temperatures, moving parts, and hydraulic pressures.
| Material | Melting Temperature (°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Common Applications | Special Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | 210-270 | 40 | Automotive, electronics | Good impact resistance |
| Polypropylene | 160-260 | 35 | Packaging, containers | Chemical resistance |
| Polycarbonate | 280-320 | 65 | Optical, medical | High transparency |
| Nylon | 260-290 | 85 | Mechanical parts | Wear resistance |
Future Trends and Developments
Automation and Robotics Integration
The integration of robotics and automation systems with injection molding machines continues to advance, enabling fully automated production cells. Robotic systems handle part removal, inspection, secondary operations, and packaging, reducing labor costs and improving consistency. Vision systems and artificial intelligence are increasingly being incorporated for quality control and process optimization, further enhancing manufacturing efficiency.
Additive Manufacturing Hybrid Solutions
Emerging technologies are bridging the gap between injection molding and additive manufacturing. Hybrid machines that combine both technologies are being developed, allowing manufacturers to create complex molds using 3D printing while maintaining the high-volume production capabilities of traditional injection molding. These innovations promise to reduce lead times for mold production and enable greater design flexibility.

Conclusion
Plastic injection molding machines continue to evolve, incorporating advanced technologies that improve efficiency, precision, and sustainability. From traditional hydraulic workhorses to sophisticated electric and hybrid systems, these machines remain fundamental to modern manufacturing across numerous industries. As technology advances, we can expect further innovations in automation, material science, and digital integration, ensuring that injection molding remains a vital manufacturing process for years to come.
