
Maintenance and Safety Protocols for Electronics Assembly Robots
Electronics assembly robots are critical components in modern manufacturing, enabling high precision, speed, and consistency in tasks such as soldering, component placement, and PCB handling. However, their optimal performance and longevity depend on rigorous maintenance and safety protocols. This article outlines essential practices to ensure operational efficiency and protect personnel.
1. Routine Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of assembly robots. Key procedures include:
1.1 Daily Checks
Operators should perform visual inspections before each shift. This includes checking for loose cables, abnormal noises, and ensuring that end-effectors (e.g., grippers) are clean and functional.

1.2 Lubrication and Calibration
Robots require periodic lubrication of joints and linear guides to reduce friction. Calibration of sensors and positioning systems ensures accuracy in component placement. Follow the manufacturer’s schedule—typically every 500 operating hours.
1.3 Software Updates and Backup
Keep robot control software updated to patch vulnerabilities and improve functionality. Regularly back up configuration files to prevent data loss.
| Task | Frequency | Responsible Party |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect mechanical components for wear | Weekly | Technician |
| Update control software | Monthly | Engineer |
| Full system calibration | Quarterly | Senior Technician |
2. Safety Protocols for Personnel
Safety is paramount when working with robots. Implement these protocols to prevent accidents:
2.1 Risk Assessment and Training
Conduct risk assessments to identify potential hazards (e.g., pinch points, electrical risks). All personnel must receive training on emergency stop procedures and safe work practices.

2.2 Physical Safeguards
Install physical barriers, light curtains, or interlocks to restrict access to the robot’s work envelope during operation. Clearly mark hazardous zones with floor tape or signs.
2.3 Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedures
Before maintenance, de-energize the robot and follow LOTO protocols to prevent accidental startup. Use locks and tags to isolate energy sources.
| Hazard | Risk | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Moving parts | Crush injuries | Physical guards |
| Electrical systems | Shock hazards | Regular insulation checks |
| High-temperature tools | Burns | Thermal barriers |
3. Predictive Maintenance Technologies
Advanced technologies like IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics enable predictive maintenance. Vibration sensors, thermal cameras, and performance monitoring can detect anomalies before failures occur.
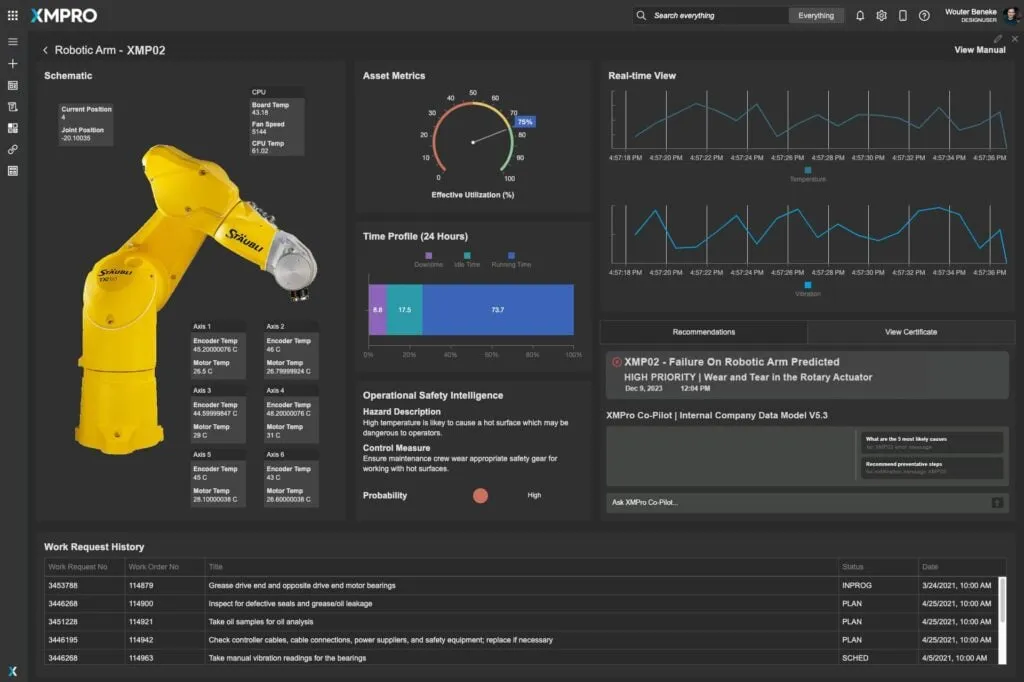
4. Documentation and Compliance
Maintain detailed logs of all maintenance activities, incidents, and repairs. Ensure compliance with international standards such as ISO 10218 (Robotics Safety) and OSHA guidelines.
Conclusion
Adhering to structured maintenance and safety protocols is essential for maximizing the efficiency and safety of electronics assembly robots. Regular upkeep, combined with robust safety measures, reduces operational risks and enhances productivity.
