
Key Benefits of Implementing Automated Assembly Equipment
Introduction to Automated Assembly Systems
Automated assembly equipment represents a transformative approach to manufacturing that leverages technology to streamline production processes. These systems integrate robotics, conveyor systems, precision tools, and sophisticated control systems to create efficient assembly lines that operate with minimal human intervention. The implementation of automated assembly equipment has become increasingly crucial for manufacturers seeking to maintain competitive advantages in today's global market.
The evolution of automated assembly has progressed from simple mechanical systems to highly sophisticated, computer-controlled operations that can adapt to varying production requirements. This technological advancement has enabled manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of precision, speed, and consistency in their assembly operations.
Enhanced Production Efficiency and Output
Increased Production Speed
Automated assembly systems operate at consistent speeds without the limitations of human physical endurance. These systems can work continuously through shifts, significantly increasing overall production capacity. The elimination of manual handling and positioning tasks reduces cycle times, allowing for faster completion of assembly operations.
Reduced Downtime
Modern automated equipment features predictive maintenance capabilities and quick changeover systems that minimize production interruptions. Automated systems can often identify potential issues before they cause significant downtime, enabling proactive maintenance scheduling and reducing unexpected production halts.
| Metric | Manual Assembly | Automated Assembly | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Units per Hour | 45 | 120 | 167% |
| Error Rate | 2.5% | 0.1% | 96% reduction |
| Operating Hours/Day | 16 (2 shifts) | 24 (continuous) | 50% increase |
| Changeover Time | 45 minutes | 5 minutes | 89% reduction |

Improved Product Quality and Consistency
Precision and Accuracy
Automated assembly equipment performs tasks with microscopic precision that exceeds human capabilities. These systems maintain consistent torque application, component placement accuracy, and assembly pressure throughout production runs, eliminating the variability inherent in manual operations.
Quality Control Integration
Advanced vision systems and sensors integrated into automated assembly lines can perform real-time quality inspections during the assembly process. This immediate feedback loop allows for instant detection and correction of defects, preventing the accumulation of errors in subsequent assembly stages.
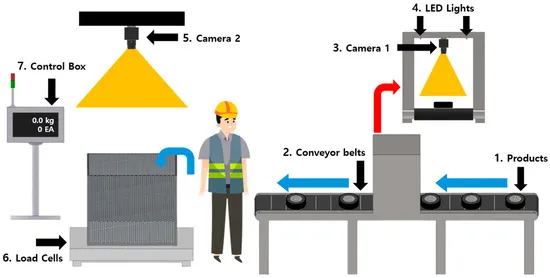
Labor Cost Reduction and Workforce Optimization
Direct Labor Cost Savings
While the initial investment in automated equipment can be substantial, the long-term reduction in labor costs provides significant return on investment. Automated systems can perform the work of multiple operators while requiring minimal supervision, leading to substantial savings in wages, benefits, and training expenses.
Workforce Reallocation
Implementation of automation allows companies to redeploy human workers to higher-value tasks such as equipment supervision, quality assurance, process improvement, and technical support. This strategic reallocation enhances overall operational efficiency and employee satisfaction.
| Cost Category | Manual Assembly | Automated Assembly | Five-Year Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Labor Costs | $1,250,000 | $375,000 | $875,000 |
| Quality-related Costs | $185,000 | $25,000 | $160,000 |
| Training Expenses | $75,000 | $30,000 | $45,000 |
| Equipment Maintenance | $40,000 | $85,000 | -$45,000 |
| Total Five-Year Cost | $1,550,000 | $515,000 | $1,035,000 |
Enhanced Workplace Safety
Reduction in Workplace Injuries
Automated systems handle repetitive, strenuous, and potentially hazardous tasks that traditionally contribute to workplace injuries. By removing human workers from dangerous operations such as heavy lifting, exposure to harmful substances, and repetitive stress activities, companies can significantly reduce accident rates and associated costs.
Ergonomic Improvements
Automation eliminates the need for workers to maintain awkward postures or perform repetitive motions for extended periods. This reduction in ergonomic risk factors leads to decreased incidence of musculoskeletal disorders and related workers' compensation claims.
Scalability and Flexibility
Adaptable Production Capacity
Modern automated assembly systems can be easily scaled to accommodate fluctuating production demands. Modular designs allow for incremental expansion or reconfiguration of assembly lines without significant downtime or capital investment in entirely new systems.
Rapid Product Changeover
Advanced automated systems feature quick-change tooling and programmable settings that enable rapid transitions between different product configurations. This flexibility allows manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands and product variations without sacrificing efficiency.

Data Collection and Process Optimization
Real-time Performance Monitoring
Automated assembly equipment generates comprehensive data on production metrics, equipment performance, and quality indicators. This data enables continuous monitoring of key performance indicators and provides valuable insights for process optimization.
Predictive Analytics
The integration of IoT sensors and data analytics platforms allows for predictive maintenance scheduling, quality trend analysis, and production forecasting. These capabilities enable proactive decision-making and continuous improvement of assembly processes.
| Metric Category | Specific Metrics | Data Collection Frequency | Primary Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Efficiency | Cycle time, OEE, Throughput | Real-time | Process optimization, Capacity planning |
| Quality Assurance | Defect rates, Tolerance measurements | Per unit | Quality control, Supplier evaluation |
| Equipment Health | Temperature, Vibration, Energy consumption | Continuous | Predictive maintenance, Downtime reduction |
| Resource Utilization | Material usage, Tool wear, Energy efficiency | Per shift | Cost reduction, Sustainability initiatives |
Competitive Advantage and Market Positioning
Enhanced Responsiveness to Market Demands
Companies implementing automated assembly systems gain significant advantages in responding to changing market conditions. The increased production flexibility, reduced lead times, and consistent quality enable faster response to customer demands and market opportunities.
Technological Leadership
Investment in advanced automation technology positions companies as industry innovators, enhancing their reputation among customers, suppliers, and investors. This technological leadership can translate into increased market share and premium pricing capabilities.

Conclusion: Strategic Implementation Considerations
The implementation of automated assembly equipment offers comprehensive benefits that extend across all aspects of manufacturing operations. From significant cost savings and quality improvements to enhanced safety and competitive positioning, the advantages are substantial and multifaceted. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, employee training, and ongoing maintenance to maximize return on investment.
Companies considering automation should conduct thorough analyses of their specific operational requirements, production volumes, and financial capabilities. A phased implementation approach, combined with strategic workforce development, can ensure smooth transition and optimal utilization of automated assembly systems.
As manufacturing continues to evolve toward Industry 4.0 standards, the integration of automated assembly equipment will become increasingly essential for maintaining competitiveness in global markets. The organizations that strategically implement and continuously optimize these systems will be best positioned for long-term success and growth.
