In today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the ability to adapt quickly to market changes, customize products, and maintain high efficiency is paramount. Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) have emerged as a transformative solution, combining computer-controlled equipment, automated material handling, and sophisticated software to create highly adaptable production environments. Unlike traditional fixed automation, FMS can manufacture a variety of parts with minimal downtime, making them indispensable for industries ranging from automotive to electronics.

Core Components of a Flexible Manufacturing System
An FMS is a complex integration of several key subsystems that work in harmony. Understanding these components is essential to appreciating how flexibility is achieved.
1. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machines
CNC machines, such as milling centers, lathes, and grinders, form the primary workhorses of an FMS. They are programmed to perform various operations on different parts without manual intervention. Their precision and programmability allow for rapid changeovers.
2. Automated Material Handling Systems (AMHS)
These systems, including automated guided vehicles (AGVs), conveyors, and robotic transfer mechanisms, move raw materials, tools, and finished parts between workstations. They ensure a continuous flow, reducing idle time and human handling.
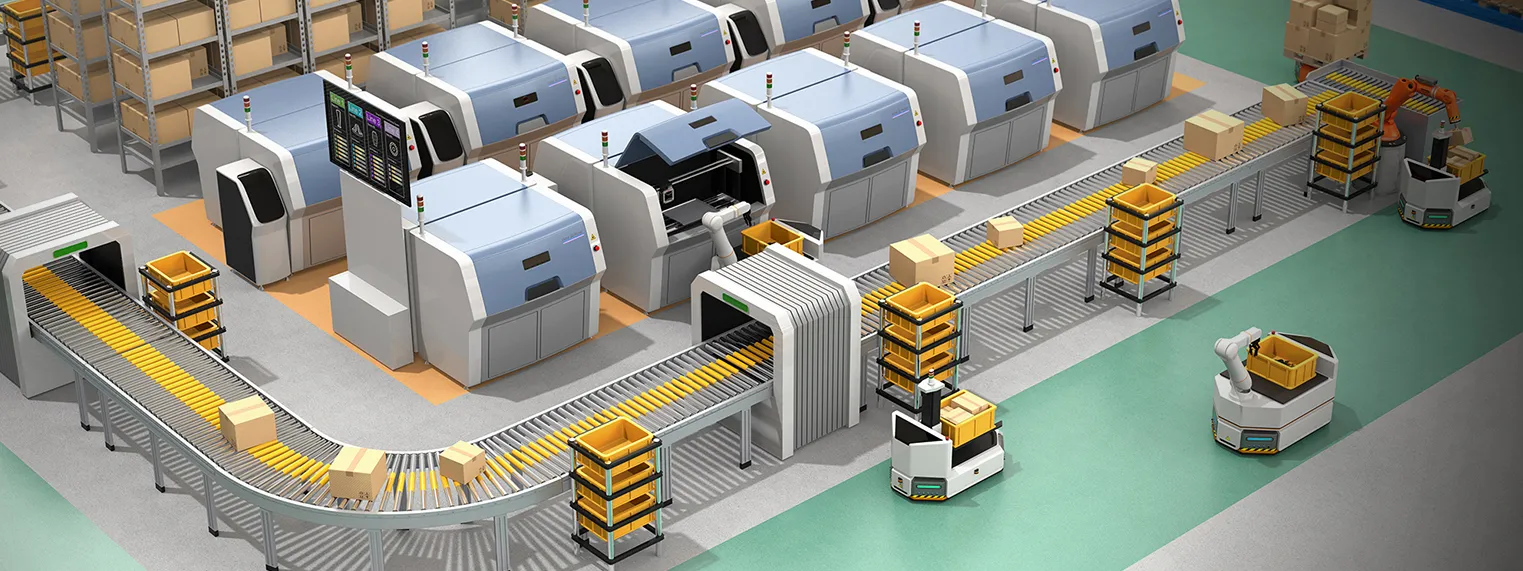

3. Central Control Computer & Software
The brain of the FMS is a central computer running specialized software for production scheduling, tool management, machine monitoring, and data collection. This system coordinates all activities in real-time, optimizing the production process.
4. Tool Management Systems
Automated tool changers and central tool storage racks allow machines to access a wide array of tools automatically. This capability is crucial for producing different parts without prolonged setup delays.
Key Benefits and Advantages of Implementing FMS
The adoption of FMS offers compelling advantages that address many challenges of modern manufacturing.
| Benefit Category | Description | Typical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Flexibility | Ability to produce multiple product types and handle design changes quickly. | Reduces time-to-market for new products by up to 70%. |
| Improved Efficiency | High machine utilization (often above 85%) and reduced non-productive time. | Increases overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) significantly. |
| Reduced Labor Costs | Automation of material handling, loading/unloading, and monitoring tasks. | Can lower direct labor requirements by 30-50%. |
| Consistent Quality | Computer control minimizes human error and ensures repeatable precision. | Dramatically reduces defect rates and rework. |
| Scalability | Modules can be added or reconfigured to scale production capacity. | Enables gradual expansion without major system overhauls. |

Challenges in FMS Implementation
Despite their advantages, deploying an FMS is a significant undertaking with notable challenges.
High Initial Investment
The cost of advanced machinery, software, and integration is substantial, requiring a clear business case and ROI analysis.
Complex System Integration
Ensuring seamless communication between machines, robots, and control systems demands expertise and careful planning.
Skilled Workforce Requirements
Operating and maintaining an FMS requires personnel skilled in robotics, programming, and systems engineering, necessitating ongoing training.
The Future: FMS and Industry 4.0
FMS is evolving into even more intelligent systems through integration with Industry 4.0 technologies. The Internet of Things (IoT) enables real-time machine data collection for predictive maintenance. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning optimize production scheduling dynamically. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is being incorporated into FMS lines for unprecedented hybrid production capabilities. This convergence is leading to the development of "smart factories" where systems are self-optimizing and fully adaptive.
Conclusion
Flexible Manufacturing Systems represent a cornerstone of modern industrial strategy. By providing the agility to respond to volatile markets, the efficiency to maximize resources, and the quality to meet high standards, FMS empowers manufacturers to thrive in a competitive global economy. As technology advances, their role will only become more central, driving the next wave of manufacturing innovation and productivity.

