
Cost Efficiency Achieved with Smart Food Processing Automation
The food processing industry is undergoing a transformative shift driven by the integration of smart automation technologies. In an era marked by rising operational costs, stringent safety regulations, and volatile market demands, achieving cost efficiency is paramount for sustainability and competitiveness. Smart automation—encompassing robotics, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics—offers a robust solution to streamline processes, reduce waste, and optimize resource utilization. This article explores how intelligent automation systems are revolutionizing cost structures in food processing, delivering significant financial benefits while enhancing product quality and operational agility.
1. The Foundation of Smart Automation in Food Processing
Smart food processing automation refers to the use of connected, intelligent systems that can monitor, control, and optimize production activities with minimal human intervention. These systems leverage real-time data from sensors embedded in machinery, production lines, and storage units to make informed decisions. Key components include:
- Industrial IoT Sensors: Track temperature, humidity, flow rates, and equipment performance.
- Robotic Arms and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Handle repetitive tasks such as sorting, packaging, and palletizing.
- AI and Machine Learning Algorithms: Predict maintenance needs, optimize recipes, and detect quality anomalies.
- Cloud Computing and Data Analytics Platforms: Aggregate and analyze data for actionable insights.
By integrating these technologies, food processors can transition from reactive to proactive operations, minimizing downtime and maximizing throughput.

2. Key Areas of Cost Reduction through Automation
Smart automation targets several critical cost centers in food processing, leading to substantial savings.
2.1 Labor Cost Optimization
Labor constitutes a significant portion of operational expenses. Automation reduces dependency on manual labor for repetitive, physically demanding, or precision-based tasks. For instance, automated cutting and deboning systems can process meat with higher speed and accuracy than human workers, reducing labor costs by up to 30-50% in specific segments. Moreover, automation allows human workers to be upskilled for supervisory, maintenance, and quality control roles, enhancing overall productivity.
2.2 Energy and Utility Savings
Energy consumption is a major cost driver in food processing, especially in heating, cooling, and refrigeration. Smart automation systems optimize energy use by dynamically adjusting equipment operation based on real-time demand. IoT-enabled sensors can monitor energy usage patterns and identify inefficiencies, while AI algorithms can schedule high-energy processes during off-peak hours. Such measures can lead to energy cost reductions of 15-25% annually.
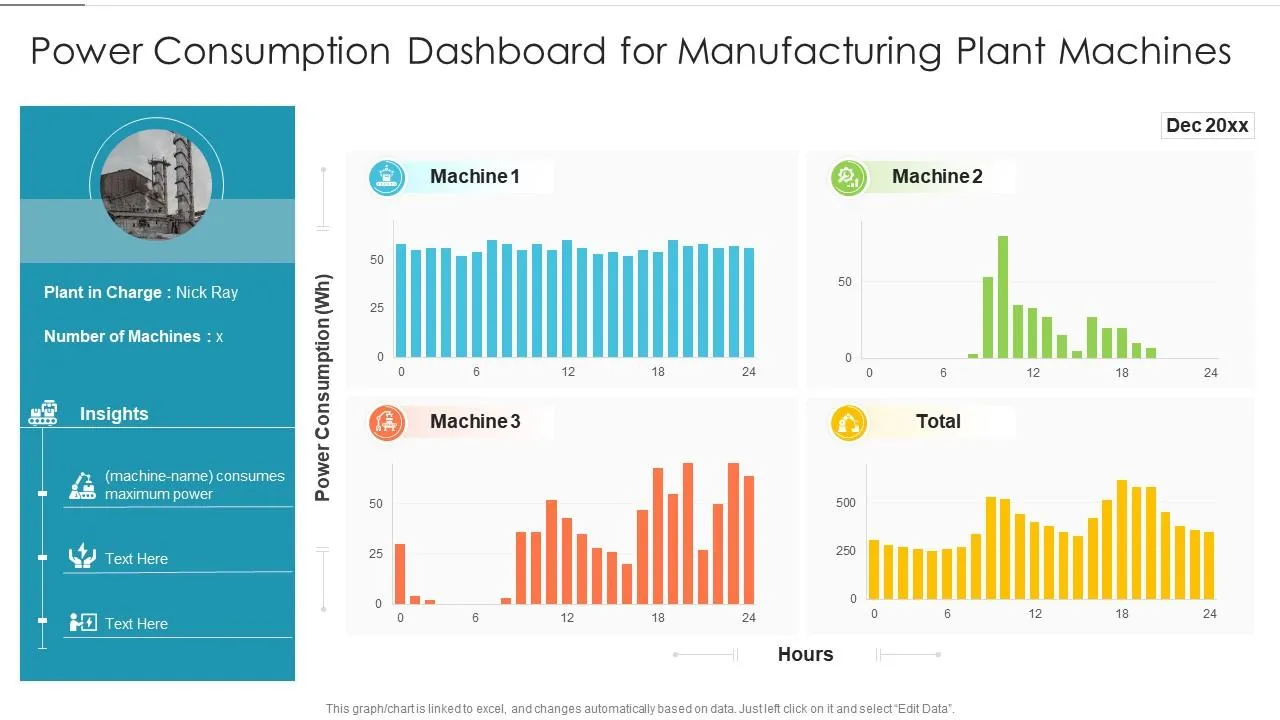
2.3 Waste Minimization and Yield Improvement
Food waste directly impacts profitability. Automated vision systems and AI-powered quality control can inspect products at high speeds, identifying defects or contaminants that might be missed by human eyes. This reduces waste from rejected batches and improves yield. For example, in vegetable processing, automated sorting systems can precisely grade produce by size, color, and quality, ensuring optimal utilization and reducing raw material waste by 10-20%.
2.4 Maintenance Cost Reduction via Predictive Analytics
Unplanned equipment downtime is costly. Smart automation enables predictive maintenance by continuously monitoring machine health. Vibration sensors, thermal cameras, and performance data feed into AI models that predict failures before they occur, allowing for scheduled maintenance during non-production hours. This approach can decrease maintenance costs by 20-30% and extend machinery lifespan.
3. Quantitative Impact: Cost Savings Analysis
The following table illustrates typical cost savings achieved through the implementation of smart automation technologies in a mid-sized food processing plant:
| Cost Category | Traditional System (Annual Cost) | With Smart Automation (Annual Cost) | Estimated Savings | Primary Automation Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labor | $1,200,000 | $800,000 | $400,000 (33.3%) | Robotics, AGVs |
| Energy | $600,000 | $480,000 | $120,000 (20%) | IoT Sensors, AI Optimization |
| Raw Material Waste | $400,000 | $320,000 | $80,000 (20%) | Computer Vision, Automated Sorting |
| Maintenance & Downtime | $300,000 | $210,000 | $90,000 (30%) | Predictive Analytics |
| Quality Control & Rejects | $250,000 | $150,000 | $100,000 (40%) | AI Inspection Systems |
| Total | $2,750,000 | $1,960,000 | $790,000 (28.7%) | Integrated Smart Systems |
Note: Figures are illustrative based on industry case studies. Actual savings depend on scale, existing infrastructure, and implementation strategy.
4. Enhancing Operational Efficiency and Flexibility
Beyond direct cost savings, smart automation improves overall operational efficiency. Automated production lines can quickly adapt to different product recipes or packaging formats through programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and digital twins. This flexibility reduces changeover time from hours to minutes, enabling manufacturers to respond swiftly to market trends and custom orders. Furthermore, data analytics provide insights into production bottlenecks, allowing for continuous process optimization.
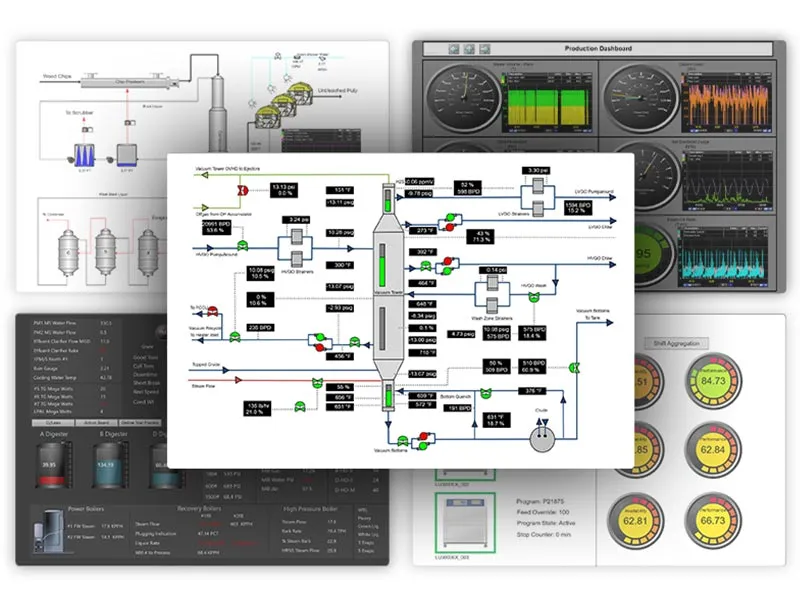
5. Challenges and Considerations for Implementation
While the benefits are compelling, adopting smart automation requires careful planning. Initial capital investment can be high, though ROI is typically achieved within 2-4 years. Integration with legacy systems may pose technical challenges, necessitating phased implementation. Workforce training is essential to manage new technologies, and data security must be prioritized to protect sensitive production information. Selecting scalable, vendor-agnostic solutions ensures long-term viability.
6. The Future: Autonomous Food Processing Plants
The future points toward fully autonomous "lights-out" processing facilities where operations run 24/7 with minimal human oversight. Advances in AI, machine learning, and collaborative robotics (cobots) will further drive down costs and enhance precision. As technology costs decrease and capabilities expand, smart automation will become accessible even to small and medium-sized enterprises, democratizing cost efficiency across the industry.
In conclusion, smart food processing automation is not merely a technological upgrade but a strategic imperative for cost management. By reducing labor, energy, waste, and maintenance expenses while boosting yield and flexibility, it delivers a powerful competitive edge. Companies that embrace this digital transformation will be best positioned to thrive in the dynamic global food market.
