
Comparing Traditional and Automated 3D Printing Systems
The evolution of 3D printing technology has revolutionized manufacturing, prototyping, and product development across numerous industries. As this technology matures, a significant distinction has emerged between traditional 3D printing systems and their increasingly sophisticated automated counterparts. This comprehensive analysis examines the key differences, advantages, and limitations of both approaches to help organizations make informed decisions about their additive manufacturing investments.
Fundamental Operational Differences
Traditional 3D printing systems typically require substantial manual intervention at multiple stages of the printing process. Operators must manually load filament, calibrate the build plate, initiate prints, remove completed objects, and perform post-processing tasks. These systems are often standalone units with limited connectivity and minimal integration with other manufacturing systems.

In contrast, automated 3D printing systems incorporate robotics, advanced software, and integrated material handling to minimize human intervention. These systems can automatically switch between materials, remove completed prints, and even perform basic post-processing operations. Many feature continuous printing capabilities, allowing for uninterrupted production cycles that significantly increase throughput.
Key Technical Specifications Comparison
| Feature | Traditional 3D Printing | Automated 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Operator Intervention | High - Manual setup and removal | Low - Automated processes |
| Production Continuity | Limited by manual operations | Continuous printing capability |
| Material Handling | Manual filament changes | Automatic material switching |
| Software Integration | Basic standalone operation | Advanced fleet management |
| Post-processing | Manual removal and finishing | Integrated part handling |
Productivity and Efficiency Analysis
Traditional System Workflow
Traditional 3D printers operate on a batch processing model where each print job requires individual attention. The workflow typically involves: design preparation, manual file transfer, printer setup, monitoring during printing, manual part removal, and post-processing. This approach creates significant downtime between jobs and limits the scalability of production operations.
Automated System Workflow
Automated systems streamline the entire production process through integrated software platforms that manage multiple printers simultaneously. These systems can queue numerous jobs, optimize build plate utilization, and schedule production based on priority and material availability. The reduction in manual tasks translates to higher equipment utilization rates and lower labor costs per printed part.
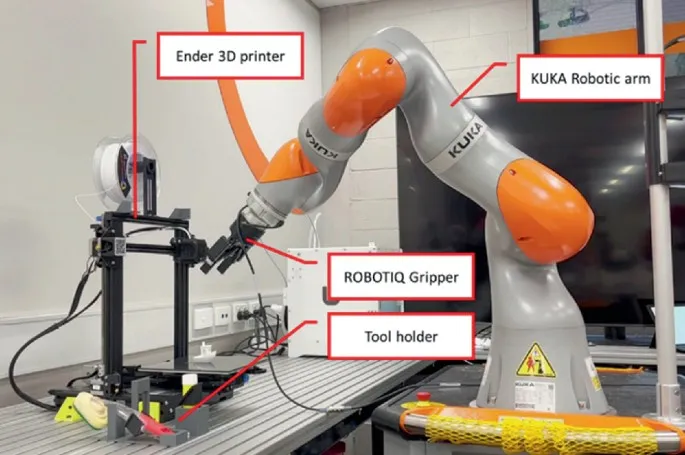
Economic Considerations
The economic comparison between traditional and automated 3D printing systems extends beyond initial acquisition costs. While automated systems typically command higher upfront investments, they offer compelling returns through reduced labor requirements, higher throughput, and improved consistency. The total cost of ownership calculation must consider operational expenses over the equipment's lifespan, including maintenance, material waste, and energy consumption.
| Cost Factor | Traditional Systems | Automated Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | $1,000 - $10,000 | $20,000 - $100,000+ |
| Labor Cost/Print Hour | $5 - $15 | $1 - $3 |
| Monthly Throughput | 50 - 200 hours | 500 - 2000+ hours |
| Material Waste | 5-15% | 2-8% |
Quality and Consistency
Traditional 3D printing systems are susceptible to variations in print quality due to manual calibration inconsistencies and operator-dependent processes. Print quality can vary between different operators and even between different print jobs handled by the same operator.
Automated systems deliver superior consistency through standardized processes, automated calibration, and continuous monitoring. Integrated sensors and cameras can detect printing anomalies in real-time, allowing for immediate corrections or automatic job restarts. This consistency is particularly valuable for production applications where part-to-part uniformity is critical.
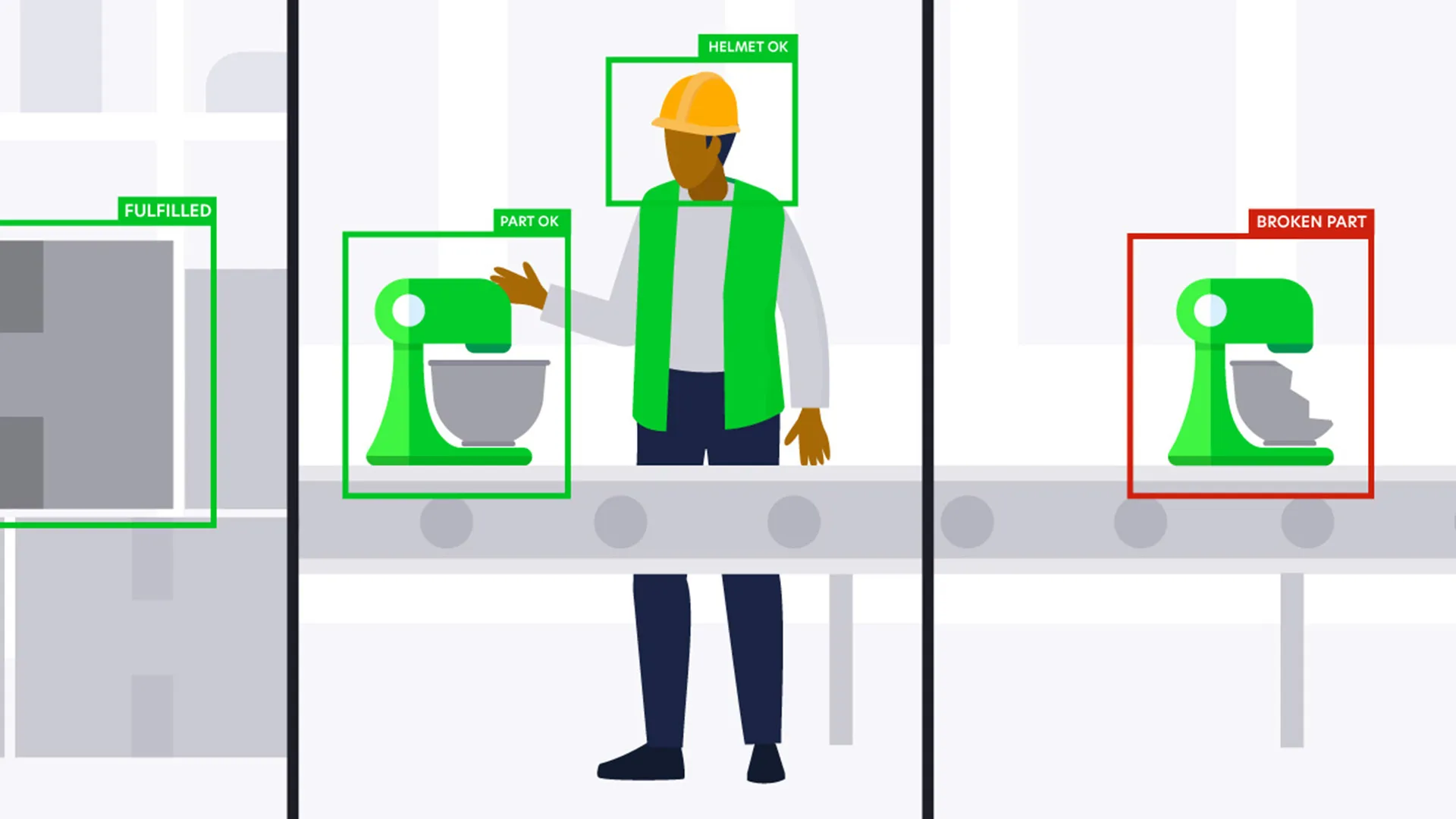
Implementation Challenges
Traditional System Challenges
While traditional 3D printers have lower barriers to entry, they present scalability limitations. As production demands increase, organizations face rising labor costs, space constraints from multiple standalone units, and management complexities. The reliance on skilled operators also creates vulnerability to workforce availability and training requirements.
Automated System Challenges
Automated 3D printing systems require significant upfront planning, infrastructure preparation, and specialized technical expertise. Integration with existing manufacturing systems can be complex, and the sophisticated nature of these systems demands dedicated maintenance resources. The higher initial investment also represents a substantial financial commitment that requires careful justification.
Future Development Trajectories
The divergence between traditional and automated 3D printing systems is likely to accelerate as technology advances. Traditional systems are evolving toward greater user-friendliness and reliability for educational, hobbyist, and small business applications. Meanwhile, automated systems are incorporating artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced robotics to create increasingly autonomous manufacturing cells that can operate with minimal human supervision.
Conclusion
The choice between traditional and automated 3D printing systems depends on specific application requirements, production volumes, and strategic objectives. Traditional systems offer accessibility and flexibility for low-volume applications, while automated systems provide scalability and efficiency for production environments. As the technology landscape continues to evolve, organizations must carefully evaluate their current and future needs to select the most appropriate 3D printing approach for their specific circumstances.
Understanding the operational characteristics, economic implications, and technical capabilities of both traditional and automated 3D printing systems enables manufacturers to make strategic decisions that align with their production goals and resource constraints. The ongoing convergence of additive manufacturing with industrial automation promises to further blur the lines between these categories, creating new opportunities for innovation across the manufacturing sector.
