
Assembly Robots in Modern Manufacturing: Examples and Applications
Assembly robots represent one of the most significant advancements in industrial automation, transforming how products are manufactured across various industries. These sophisticated machines have evolved from simple mechanical arms to highly intelligent systems capable of performing complex assembly tasks with precision and efficiency.
Types of Assembly Robots and Their Applications
Articulated Robots
Articulated robots feature rotary joints and resemble human arms, typically with four to six axes of movement. These versatile robots excel in complex assembly tasks requiring multiple angles and orientations.

SCARA Robots
Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm (SCARA) robots are specifically designed for high-speed assembly operations. Their rigid vertical structure and compliant horizontal movement make them ideal for precision tasks in electronics manufacturing.
Delta Robots
Delta robots, with their parallel arm structure, offer exceptional speed and accuracy for lightweight assembly tasks. They are commonly used in packaging, food processing, and pharmaceutical industries.
Real-World Assembly Robot Examples
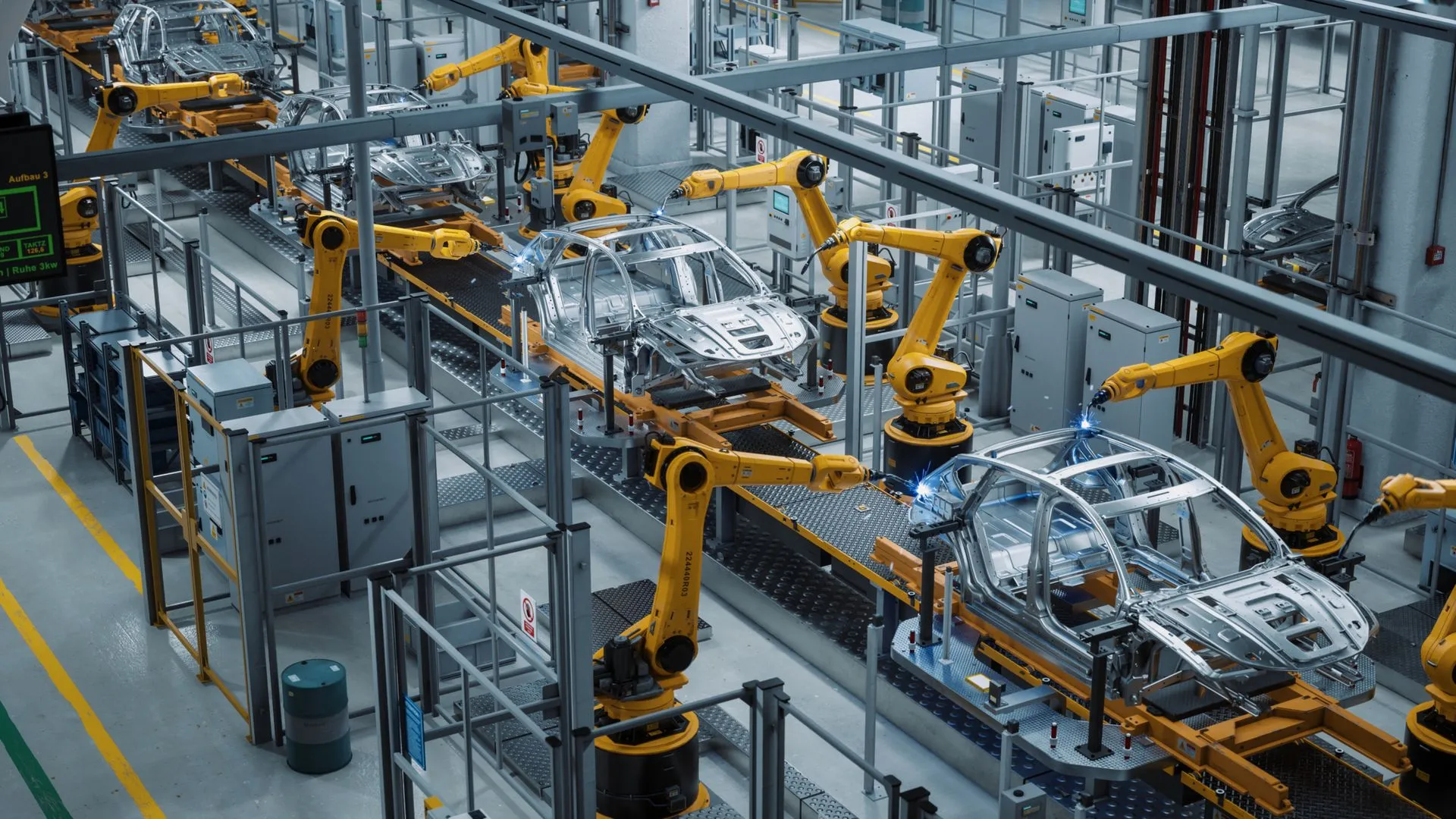
Automotive Industry Applications
The automotive sector has been at the forefront of adopting assembly robots. Major manufacturers like Toyota, Ford, and Tesla utilize sophisticated robotic systems for various assembly operations.
| Application | Robot Type | Key Benefits | Manufacturer Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Assembly | Articulated | High precision, heavy payload capacity | Fanuc M-2000iA |
| Windshield Installation | Collaborative | Safe human-robot interaction, flexibility | Universal Robots UR10 |
| Welding Operations | Articulated | Consistent quality, high speed | KUKA KR QUANTEC |
| Painting and Coating | Articulated | Uniform application, reduced waste | ABB IRB 5500 |

Electronics Manufacturing
Electronics assembly requires extreme precision and cleanliness, making robots indispensable in this sector. Companies like Samsung, Apple, and Intel rely heavily on robotic automation.
Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace industry employs specialized assembly robots for tasks requiring exceptional accuracy and reliability. These robots handle everything from component fabrication to final aircraft assembly.

Advanced Assembly Robot Technologies
Vision Systems Integration
Modern assembly robots incorporate advanced vision systems that enable them to identify components, verify assembly quality, and adapt to variations in part placement.
Force Sensing and Compliance
Advanced force sensors allow robots to apply precise amounts of pressure during assembly operations, preventing damage to delicate components and ensuring proper fit.
Collaborative Robotics
Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human operators, combining human dexterity and problem-solving skills with robotic precision and endurance.
| Technology | Function | Industry Application | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Vision Systems | Object recognition and positioning | Electronics, Automotive | Handles complex geometries |
| Torque Sensors | Force feedback and control | Medical Devices, Aerospace | Prevents component damage |
| AI and Machine Learning | Adaptive assembly strategies | All Industries | Continuous improvement |
| IoT Connectivity | Real-time monitoring and analytics | Smart Factories | Predictive maintenance |

Implementation Considerations for Assembly Robots
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Implementing assembly robots requires careful consideration of initial investment, operational costs, and expected return on investment. Factors include equipment costs, integration expenses, training, and maintenance.
Integration Challenges
Successful robot integration involves addressing technical compatibility, workflow optimization, and employee training. Companies must ensure seamless communication between robotic systems and existing manufacturing equipment.
Safety Requirements
Proper safety measures, including physical barriers, emergency stop systems, and safety-rated monitoring, are essential for protecting workers and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Future Trends in Assembly Robotics
Artificial Intelligence Integration
The integration of AI enables assembly robots to learn from experience, optimize processes autonomously, and handle increasingly complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
Mobile Assembly Robots
Mobile robotic platforms combined with assembly capabilities are emerging, allowing for flexible manufacturing layouts and on-demand production systems.

Sustainable Manufacturing
Assembly robots contribute to sustainable manufacturing through energy efficiency, reduced material waste, and optimized resource utilization, aligning with global environmental goals.
As assembly robot technology continues to advance, these automated systems will become even more intelligent, flexible, and accessible to manufacturers of all sizes. The ongoing development of smarter, more capable assembly robots promises to further revolutionize manufacturing processes across all industries.
